The dental emergency dental trauma are the most common in children and teenagers, and the teeth most often affected are the upper incisors. In case of permanent tooth trauma a consequences are extortion, injury of the supporting tissues of the tooth, o dislocation. This is the partial displacement of the tooth from its seat, until avulsion in which has the total expulsion of the tooth from its socket.
In other cases, the tooth fracture can be more or less serious if it involves only the hard tissues of the tooth ( enamel and dentin ), or if it also affects the pulp (the " nerve "); in the worst cases the fracture involves the root of the tooth and its recovery is difficult if not impossible.
In any case you need to go to the dentist as soon as possible : the quicker intervention is, the better is the prognosis. If it is concussion may happen that the tooth, although intact, lose its vitality, or goes into necrosis, in which case it must be devitalized; otherwise it will be necessary to do periodic inspections. In DISLOCATION the loss of viability is more likely and, in some cases, the dentist will assess the need to reposition the tooth with the orthodontic appliance.
In case of avulsion of the element, the replanting should be performed promptly, preferably made within 20 minutes after trauma.
If possible, provide for themselves, before they even arrive at the studio, following several precautions:
- Handle the tooth only by the crown;
- Wash it gently with running water or, if possible, normal saline;
- Reposition the tooth gently in socket.
If you can not perform self-replanting, we still need keep the tooth moist, saving in milk, in physiological saline solution or in the mouth in contact with the cheek, going immediately to the dentist who will perform the replanting the tooth, repositioning it in its socket and "locking" the teeth adjacent to a few weeks.
The success of replanting is closely related to the timeliness of the intervention: within a few hours because it is no longer possible to "take" of the tooth in its socket. The vitality of replanted tooth is nearly compromised.
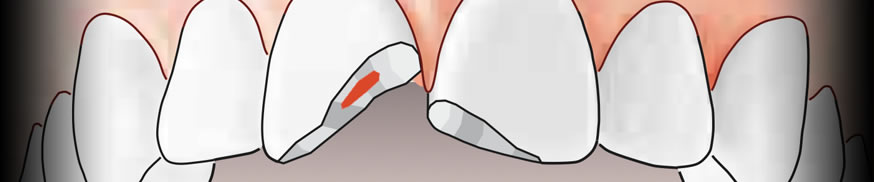
In the case of the tooth FRACTURE it is necessary to preserve the fragment that should be stored in milk or saliva; if the fragment is intact dentist will execute bonding, otherwise reconstruction composite.
If the fracture involves the pulp in most cases need devitalization, otherwise it will be periodically assessed its vitality.
In the trauma of the deciduous teeth the dentist based on the maturity of the corresponding permanent teeth will consider whether to intervene, by devitalizing extracting the affected tooth, or wait and check again. The total avulsion of deciduous generally do not involve major problems, while dislocations intrusive, in which the tooth falls within its cavity, can cause permanent damages to the corresponding tooth. The consequences can be assessed only in eruption.
A traumatized tooth that does not present any apparent damage should however be kept under observation , as anyway it can be subject to late complications, such as pulp necrosis, root resorption or ankylosis .
These cases usually are not accompanied by noise, so if the patient does not carry put periodic checks, he/she complain about the hassles too late, when the tooth is now irrecoverable..
